Multiclass classification#
The multiclass classification problem is a regression problem from an input \(x \in {\cal X}\) to discrete labels \(y\in {\cal Y}\), where \({\cal Y}\) is a discrete set of size \(C\) bigger than two (for \(C=2\) it is the more usual binary classification).
Labels are encoded in a one-hot fashion, that is if \(C=4\) and \(y=2\), we note \(\bar{y} = [0,1,0,0]\).
The generative model for this problem consists of:
\(C\) latent functions \(\mathbf{f} = [f_1,...,f_C]\) with an independent Gaussian Process prior
a deterministic function that builds a discrete distribution \(\pi(\mathbf{f}) = [\pi_1(f_1),...,\pi_C(f_C)]\) from the latents such that \(\sum_c \pi_c(f_c) = 1\)
a discrete likelihood \(p(y|\mathbf{f}) = Discrete(y;\pi(\mathbf{f})) = \prod_c \pi_c(f_c)^{\bar{y}_c}\)
A typical example of \(\pi\) is the softmax function:
\begin{equation} \pi_c (f_c) \propto \exp( f_c) \end{equation}
Another convenient one is the robust max: \begin{equation} \pi_c(\mathbf{f}) = \begin{cases} 1 - \epsilon, & \mbox{if } c = \arg \max_c f_c \\ \epsilon /(C-1), & \mbox{ otherwise} \end{cases} \end{equation}
[1]:
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # ignore DeprecationWarnings from tensorflow
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from multiclass_classification import colors, plot_posterior_predictions
import gpflow
from gpflow.ci_utils import reduce_in_tests
from gpflow.utilities import print_summary, set_trainable
%matplotlib inline
# reproducibility:
np.random.seed(0)
tf.random.set_seed(123)
2023-05-03 23:15:20.817622: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:193] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX2 AVX512F FMA
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
2023-05-03 23:15:20.980805: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-05-03 23:15:20.980848: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.
2023-05-03 23:15:21.010461: E tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:2981] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
2023-05-03 23:15:21.884583: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-05-03 23:15:21.884646: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer_plugin.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer_plugin.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-05-03 23:15:21.884654: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Cannot dlopen some TensorRT libraries. If you would like to use Nvidia GPU with TensorRT, please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly.
Sampling from the GP multiclass generative model#
Declaring model parameters and input#
[2]:
# Number of functions and number of data points
C = 3
N = 100
# Lengthscale of the SquaredExponential kernel (isotropic -- change to `[0.1] * C` for ARD)
lengthscales = 0.1
# Jitter
jitter_eye = np.eye(N) * 1e-6
# Input
X = np.random.rand(N, 1)
Sampling#
[3]:
# SquaredExponential kernel matrix
kernel_se = gpflow.kernels.SquaredExponential(lengthscales=lengthscales)
K = kernel_se(X) + jitter_eye
# Latents prior sample
f = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=np.zeros(N), cov=K, size=(C)).T
# Hard max observation
Y = np.argmax(f, 1).flatten().astype(int)
# One-hot encoding
Y_hot = np.zeros((N, C), dtype=bool)
Y_hot[np.arange(N), Y] = 1
data = (X, Y)
2023-05-03 23:15:25.496731: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcuda.so.1'; dlerror: libcuda.so.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2023-05-03 23:15:25.496767: W tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:263] failed call to cuInit: UNKNOWN ERROR (303)
2023-05-03 23:15:25.496789: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_diagnostics.cc:156] kernel driver does not appear to be running on this host (cd73b4568ef0): /proc/driver/nvidia/version does not exist
2023-05-03 23:15:25.497043: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:193] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX2 AVX512F FMA
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
Plotting#
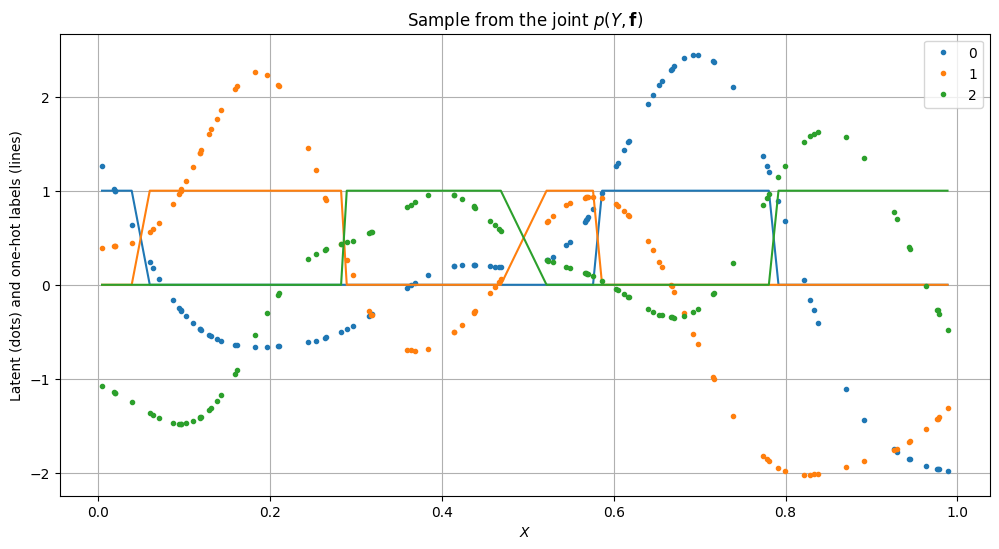
[4]:
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
order = np.argsort(X.flatten())
for c in range(C):
plt.plot(X[order], f[order, c], ".", color=colors[c], label=str(c))
plt.plot(X[order], Y_hot[order, c], "-", color=colors[c])
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("$X$")
plt.ylabel("Latent (dots) and one-hot labels (lines)")
plt.title("Sample from the joint $p(Y, \mathbf{f})$")
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Inference#
Inference here consists of computing the posterior distribution over the latent functions given the data \(p(\mathbf{f}|Y, X)\).
You can use different inference methods. Here we perform variational inference. For a treatment of the multiclass classification problem using MCMC sampling, see Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC).
Approximate inference: Sparse Variational Gaussian Process#
Declaring the SVGP model (see GPs for big data)#
[5]:
# sum kernel: Matern32 + White
kernel = gpflow.kernels.Matern32() + gpflow.kernels.White(variance=0.01)
# Robustmax Multiclass Likelihood
invlink = gpflow.likelihoods.RobustMax(C) # Robustmax inverse link function
likelihood = gpflow.likelihoods.MultiClass(
3, invlink=invlink
) # Multiclass likelihood
Z = X[::5].copy() # inducing inputs
m = gpflow.models.SVGP(
kernel=kernel,
likelihood=likelihood,
inducing_variable=Z,
num_latent_gps=C,
whiten=True,
q_diag=True,
)
# Only train the variational parameters
set_trainable(m.kernel.kernels[1].variance, False)
set_trainable(m.inducing_variable, False)
print_summary(m, fmt="notebook")
| name | class | transform | prior | trainable | shape | dtype | value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].variance | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 1.0 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].lengthscales | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 1.0 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[1].variance | Parameter | Softplus | False | () | float64 | 0.01 | |
| SVGP.likelihood.invlink.epsilon | Parameter | Sigmoid | Beta | False | () | float64 | 0.001 |
| SVGP.inducing_variable.Z | Parameter | Identity | False | (20, 1) | float64 | [[0.54881... | |
| SVGP.q_mu | Parameter | Identity | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[0., 0., 0.... | |
| SVGP.q_sqrt | Parameter | Softplus | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[1., 1., 1.... |
Running inference#
[6]:
opt = gpflow.optimizers.Scipy()
opt_logs = opt.minimize(
m.training_loss_closure(data),
m.trainable_variables,
options=dict(maxiter=reduce_in_tests(1000)),
)
print_summary(m, fmt="notebook")
| name | class | transform | prior | trainable | shape | dtype | value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].variance | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 136384.63633 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].lengthscales | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 0.17436 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[1].variance | Parameter | Softplus | False | () | float64 | 0.01 | |
| SVGP.likelihood.invlink.epsilon | Parameter | Sigmoid | Beta | False | () | float64 | 0.001 |
| SVGP.inducing_variable.Z | Parameter | Identity | False | (20, 1) | float64 | [[0.54881... | |
| SVGP.q_mu | Parameter | Identity | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[-0.23227, 0.61397, -0.3817... | |
| SVGP.q_sqrt | Parameter | Softplus | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[0.08248, 0.07942, 0.12069... |
[7]:
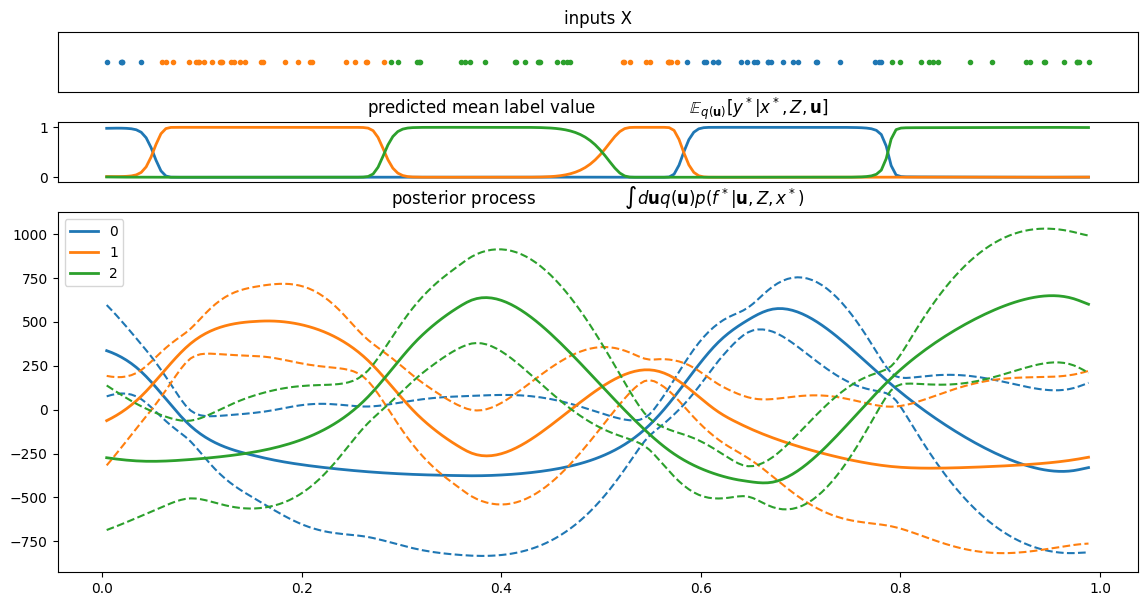
plot_posterior_predictions(m, X, Y)