Multiclass classification#
The multiclass classification problem is a regression problem from an input \(x \in {\cal X}\) to discrete labels \(y\in {\cal Y}\), where \({\cal Y}\) is a discrete set of size \(C\) bigger than two (for \(C=2\) it is the more usual binary classification).
Labels are encoded in a one-hot fashion, that is if \(C=4\) and \(y=2\), we note \(\bar{y} = [0,1,0,0]\).
The generative model for this problem consists of:
\(C\) latent functions \(\mathbf{f} = [f_1,...,f_C]\) with an independent Gaussian Process prior
a deterministic function that builds a discrete distribution \(\pi(\mathbf{f}) = [\pi_1(f_1),...,\pi_C(f_C)]\) from the latents such that \(\sum_c \pi_c(f_c) = 1\)
a discrete likelihood \(p(y|\mathbf{f}) = Discrete(y;\pi(\mathbf{f})) = \prod_c \pi_c(f_c)^{\bar{y}_c}\)
A typical example of \(\pi\) is the softmax function:
\begin{equation} \pi_c (f_c) \propto \exp( f_c) \end{equation}
Another convenient one is the robust max: :nbsphinx-math:`begin{equation} pi_c(mathbf{f}) = begin{cases} 1 - epsilon, & mbox{if } c = arg max_c f_c \
epsilon /(C-1), & mbox{ otherwise} end{cases}
end{equation}`
[1]:
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # ignore DeprecationWarnings from tensorflow
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import gpflow
from gpflow.utilities import print_summary, set_trainable
from gpflow.ci_utils import ci_niter
from multiclass_classification import plot_posterior_predictions, colors
# reproducibility:
np.random.seed(0)
tf.random.set_seed(123)
2022-05-10 10:59:22.997469: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcudart.so.11.0'; dlerror: libcudart.so.11.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2022-05-10 10:59:22.997495: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cudart_stub.cc:29] Ignore above cudart dlerror if you do not have a GPU set up on your machine.
Sampling from the GP multiclass generative model#
Declaring model parameters and input#
[2]:
# Number of functions and number of data points
C = 3
N = 100
# Lengthscale of the SquaredExponential kernel (isotropic -- change to `[0.1] * C` for ARD)
lengthscales = 0.1
# Jitter
jitter_eye = np.eye(N) * 1e-6
# Input
X = np.random.rand(N, 1)
Sampling#
[3]:
# SquaredExponential kernel matrix
kernel_se = gpflow.kernels.SquaredExponential(lengthscales=lengthscales)
K = kernel_se(X) + jitter_eye
# Latents prior sample
f = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean=np.zeros(N), cov=K, size=(C)).T
# Hard max observation
Y = np.argmax(f, 1).flatten().astype(int)
# One-hot encoding
Y_hot = np.zeros((N, C), dtype=bool)
Y_hot[np.arange(N), Y] = 1
data = (X, Y)
2022-05-10 10:59:25.484909: W tensorflow/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libcuda.so.1'; dlerror: libcuda.so.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
2022-05-10 10:59:25.484933: W tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_driver.cc:269] failed call to cuInit: UNKNOWN ERROR (303)
2022-05-10 10:59:25.484952: I tensorflow/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_diagnostics.cc:156] kernel driver does not appear to be running on this host (49c966262641): /proc/driver/nvidia/version does not exist
2022-05-10 10:59:25.485197: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:151] This TensorFlow binary is optimized with oneAPI Deep Neural Network Library (oneDNN) to use the following CPU instructions in performance-critical operations: AVX2 AVX512F FMA
To enable them in other operations, rebuild TensorFlow with the appropriate compiler flags.
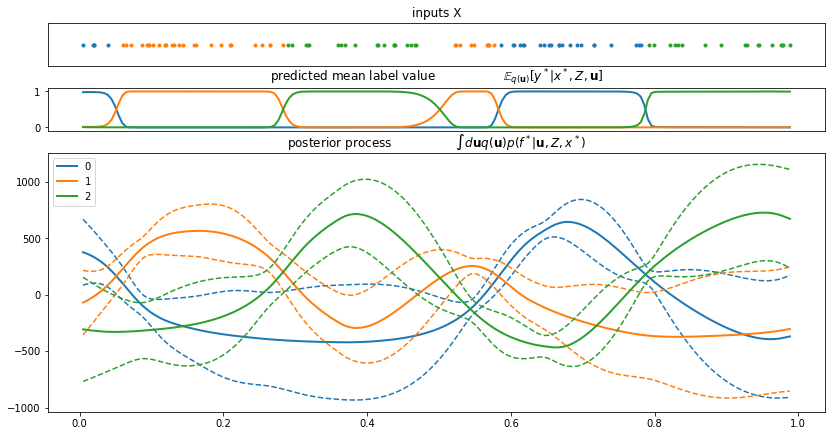
Plotting#
[4]:
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
order = np.argsort(X.flatten())
for c in range(C):
plt.plot(X[order], f[order, c], ".", color=colors[c], label=str(c))
plt.plot(X[order], Y_hot[order, c], "-", color=colors[c])
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("$X$")
plt.ylabel("Latent (dots) and one-hot labels (lines)")
plt.title("Sample from the joint $p(Y, \mathbf{f})$")
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Inference#
Inference here consists of computing the posterior distribution over the latent functions given the data \(p(\mathbf{f}|Y, X)\).
You can use different inference methods. Here we perform variational inference. For a treatment of the multiclass classification problem using MCMC sampling, see Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC).
Approximate inference: Sparse Variational Gaussian Process#
Declaring the SVGP model (see GPs for big data)#
[5]:
# sum kernel: Matern32 + White
kernel = gpflow.kernels.Matern32() + gpflow.kernels.White(variance=0.01)
# Robustmax Multiclass Likelihood
invlink = gpflow.likelihoods.RobustMax(C) # Robustmax inverse link function
likelihood = gpflow.likelihoods.MultiClass(3, invlink=invlink) # Multiclass likelihood
Z = X[::5].copy() # inducing inputs
m = gpflow.models.SVGP(
kernel=kernel,
likelihood=likelihood,
inducing_variable=Z,
num_latent_gps=C,
whiten=True,
q_diag=True,
)
# Only train the variational parameters
set_trainable(m.kernel.kernels[1].variance, False)
set_trainable(m.inducing_variable, False)
print_summary(m, fmt="notebook")
2022-05-10 10:59:25.964066: W tensorflow/python/util/util.cc:368] Sets are not currently considered sequences, but this may change in the future, so consider avoiding using them.
| name | class | transform | prior | trainable | shape | dtype | value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].variance | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 1.0 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].lengthscales | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 1.0 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[1].variance | Parameter | Softplus | False | () | float64 | 0.009999999999999998 | |
| SVGP.likelihood.invlink.epsilon | Parameter | Sigmoid | Beta | False | () | float64 | 0.0010000000000000005 |
| SVGP.inducing_variable.Z | Parameter | Identity | False | (20, 1) | float64 | [[0.5488135... | |
| SVGP.q_mu | Parameter | Identity | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[0., 0., 0.... | |
| SVGP.q_sqrt | Parameter | Softplus | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[1., 1., 1.... |
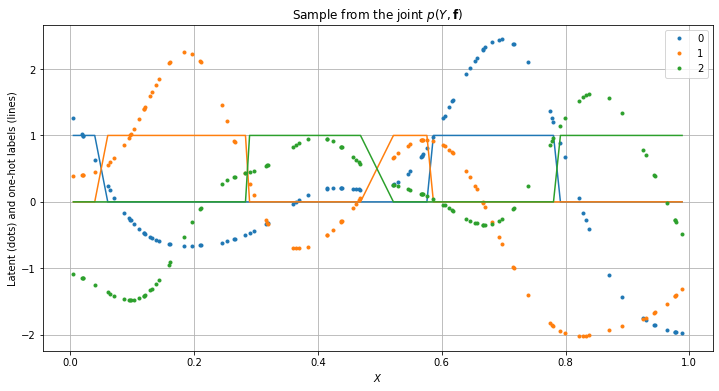
Running inference#
[6]:
opt = gpflow.optimizers.Scipy()
opt_logs = opt.minimize(
m.training_loss_closure(data), m.trainable_variables, options=dict(maxiter=ci_niter(1000))
)
print_summary(m, fmt="notebook")
| name | class | transform | prior | trainable | shape | dtype | value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].variance | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 171248.84194886775 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[0].lengthscales | Parameter | Softplus | True | () | float64 | 0.17435068075529464 | |
| SVGP.kernel.kernels[1].variance | Parameter | Softplus | False | () | float64 | 0.009999999999999998 | |
| SVGP.likelihood.invlink.epsilon | Parameter | Sigmoid | Beta | False | () | float64 | 0.0010000000000000005 |
| SVGP.inducing_variable.Z | Parameter | Identity | False | (20, 1) | float64 | [[0.5488135... | |
| SVGP.q_mu | Parameter | Identity | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[-0.23231073, 0.61401618, -0.38170545... | |
| SVGP.q_sqrt | Parameter | Softplus | True | (20, 3) | float64 | [[0.08256517, 0.07948581, 0.12075035... |
[7]:
plot_posterior_predictions(m, X, Y)